Dialogs
Since the built-in WPF dialogs are unstyleable, we had to create our own implementation. You will find our dialogs within the MahApps.Metro.Controls.Dialogs namespace.
All dialogs in MahApps.Metro are called asynchronously.
If you’re on .NET 4.5 you have the luck of using the async keyword,
if you’re stuck with .NET 4.0, you’ll have to use continuations when using the dialogs.
This tutorial uses .NET 4.5.
If you really want to use async/await with .NET 4.0 (and MahApps.Metro v1.6.5), you can install Microsoft Async
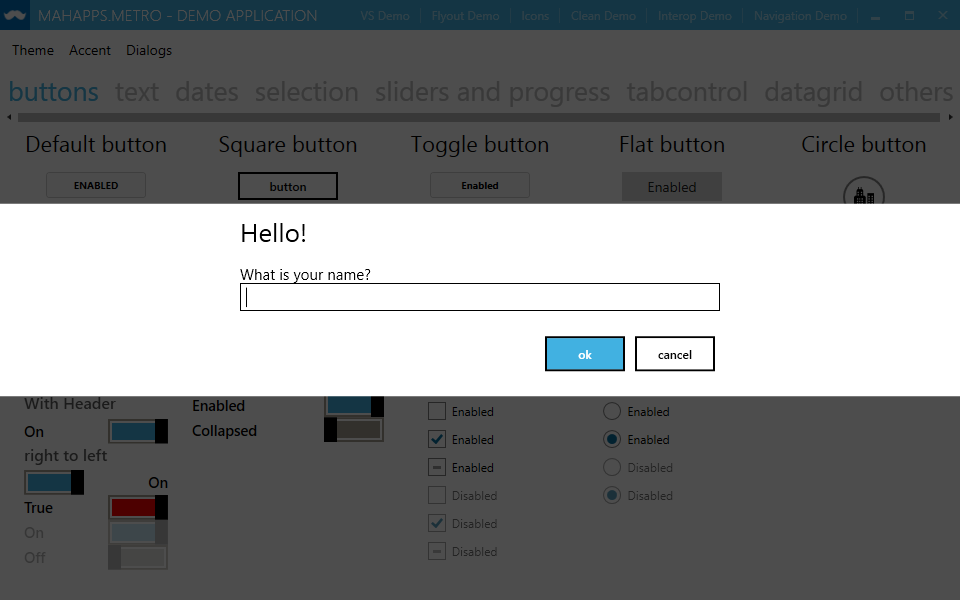
Message dialog
Simple message dialogs can be displayed with the ShowMessageAsync method. It is an extension method for MetroWindow, so call it from your window class.
await this.ShowMessageAsync("This is the title", "Some message");
There are additional optional parameters for simple buttons, such as Ok and Cancel and settings for the color theme and animation options.
Progress dialog
There is a built-in dialog that displays a progress bar at the bottom of the dialog. Call it like this:
var controller = await this.ShowProgressAsync("Please wait...", "Progress message");
This method returns a ProgressDialogController object that exposes the SetProgress method, use it to set the current progress.
A picture of the progress dialog in the demo:

Support for viewmodels
You can open dialogs from your viewmodel by using the IDialogCoordinator.
Add the following code to your Window.xaml or UserControl.xaml:
<UserControl x:Class=="...
xmlns:Dialog="clr-namespace:MahApps.Metro.Controls.Dialogs;assembly=MahApps.Metro"
Dialog:DialogParticipation.Register="{Binding}">
Your code behind in the Window.xaml.cs or UserControl.xaml.cs should look like this:
using MahApps.Metro.Controls.Dialogs;
namespace EXAMPLE
{
public class USERCONTROL : UserControl
{
// Here we create the viewmodel with the current DialogCoordinator instance
VIEWMODEL vm = new VIEWMODEL(DialogCoordinator.Instance);
public USERCONTROL()
{
InitializeComponent();
DataContext = vm;
}
}
}
Last but not least, your viewmodel:
using MahApps.Metro.Controls.Dialogs;
namespace EXAMPLE
{
public class VIEWMODEL : ViewModelBase
{
// Variable
private IDialogCoordinator dialogCoordinator;
// Constructor
public VIEWMODEL (IDialogCoordinator instance)
{
dialogCoordinator = instance;
}
// Methods
private void FooMessage()
{
await dialogCoordinator.ShowMessageAsync(this, "HEADER","MESSAGE");
}
private void FooProgress()
{
// Show...
ProgressDialogController controller = await dialogCoordinator.ShowProgressAsync(this, "HEADER", "MESSAGE");
controller.SetIndeterminate();
// Do your work...
// Close...
await controller.CloseAsync();
}
// Actions... (ICommands for your view)
}
}
